A seismic shift has hit the fitness industry this week following the release of alarming new clinical data regarding weight-loss medications. On Wednesday, researchers from Stanford’s Department of Medicine released a pivotal study indicating that without intervention, up to 40% of weight lost by patients on GLP-1 agonists—like Ozempic, Wegovy, and Zepbound—can consist of lean muscle mass rather than fat. In immediate response, major fitness chains and health organizations have issued what is being called the “GLP-1 Strength” mandate, a new standard of care that prioritizes heavy resistance training over cardio for millions of Americans.
The ‘Resistance-First’ Revolution
For decades, the standard prescription for weight loss was a mix of caloric deficit and aerobic activity. However, the new data released on January 14, 2026, has turned this wisdom on its head for the GLP-1 population. The rapid weight reduction caused by these drugs accelerates sarcopenia—the involuntary loss of skeletal muscle—at a rate three times faster than natural aging.
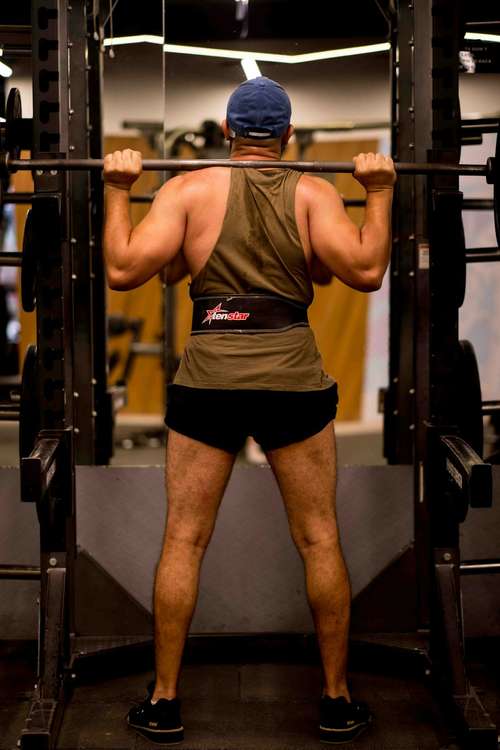
In response to these findings, luxury fitness giant Equinox and national chains like Planet Fitness have rolled out updated protocols this weekend. The core of these new guidelines is a “Resistance-First” approach, which advises that GLP-1 users dedicate their first 30 minutes of exercise solely to strength training before attempting any cardiovascular work. “The goal isn’t just to get smaller anymore; it’s to get denser,” explains Dr. Marcus Thorne, a metabolic health strategist who contributed to the new industry guidelines. “If you are on these medications, your muscle tissue is under siege. Cardio burns calories, but strength training builds the armor you need to protect your metabolism.”
Inside the New GLP-1 Strength Training Protocol
The new mandates aren't just vague suggestions; they come with a specific, science-backed prescription designed to counteract the catabolic effects of rapid weight loss. According to the guidelines released by the International Sports Sciences Association (ISSA) just yesterday, the optimal routine for GLP-1 users includes:
- Frequency: A minimum of 3 full-body resistance sessions per week.
- Intensity: Focus on “progressive overload,” lifting weights heavy enough to reach fatigue by the 8th or 10th repetition.
- Movement Selection: Prioritize compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and overhead presses that recruit the maximum amount of muscle fibers.
- The “Cardio Cap”: Limiting steady-state cardio to post-lift sessions to prevent further caloric deficits that could eat away at muscle tissue.
This protocol marks a departure from the high-intensity interval training (HIIT) trends of previous years. The focus has shifted entirely to muscle preservation and longevity. By signaling the body to retain muscle through heavy lifting, patients can force the medication to target fat stores almost exclusively.
The Hidden Dangers of ‘Ozempic Face’ and Body
The aesthetic side effects of these drugs, colloquially known as “Ozempic Face” or “Ozempic Body,” are actually symptoms of the deeper medical issue: rapid muscle wasting. When the body loses facial fat and muscle simultaneously, skin sags and appears aged. The same process happens internally to the heart and skeletal muscles.
“We are seeing patients in their 30s with the bone density and muscle quality of 70-year-olds,” warns Dr. Sarah Jenkins, a leading endocrinologist who spoke at the Converge 2025 medical conference earlier this month. “The ‘GLP-1 Strength’ mandate is not about vanity. It is about preventing a future epidemic of frailty. If you lose 20 pounds, and 8 of those pounds are muscle, you have technically lowered your weight but worsened your body composition.”
Nutrition: The Other Half of the Mandate
Alongside the workout protocols, the new 2026 guidelines emphasize a nutritional strategy that borders on aggressive. Because GLP-1 drugs suppress appetite so effectively, users often struggle to eat enough protein to sustain muscle growth. The new mandate suggests a daily protein intake of 1.2 to 1.5 grams per pound of ideal body weight—a target that requires conscious effort and often supplementation.
Why 2026 is the Year of Muscle Longevity
As we settle into 2026, the cultural conversation around fitness is fundamentally changing. The era of "thin at all costs" is over, replaced by a focus on body composition and functional longevity. With over 15% of the adult population now estimated to be using some form of weight-management pharmacotherapy, the gym is no longer just a place to burn calories—it is a pharmacy where the prescription is iron.
This “GLP-1 Strength” mandate represents the fitness industry’s most significant pivot in a decade. It acknowledges that while biotechnology can solve the appetite equation, only physical effort can solve the longevity equation. As gym floors fill up with members following these new heavy-lifting protocols, the message is clear: the medicine helps you lose the weight, but the muscle helps you keep your life.